Multiple projects regarding to Design and Analysis of Algorithms course
Designing and implementation of:
- The Closest Pair of Points Problem (Divide & Conquer)
- Sudoku Solver (Backtracking)
- Tournament Scheduler (Divide & Conquer)
- Huffman Coding (Greedy)
- Bellman–Ford (Dynamic Programming)
- Matrix Chain Multiplication (Dynamic Programming)
- N-Queens Solver (Backtracking)
- Travelling Salesman Problem (Dynamic Programming)

Closest Pair of Points Problem
- Github repo
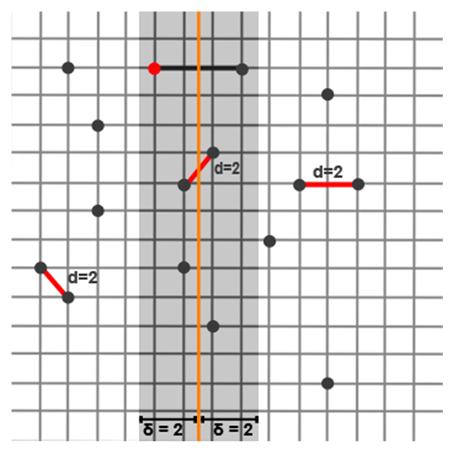
Given a list (x1, y1),(x2, y2), . . . ,(xn, yn) of points in the plane, find the pair of points that are closest together
Sophisticated Solution: We can do better with a divide-and-conquer algorithm that exploits the geometry
of distance. The idea is to split the point set into two halves with a vertical line, find the closest
pair within each half, and then find the closest pair between the two halves. The result of finding
the closest pair within each half speeds up finding the closest pair between the halves. The closest
pair is the minimum of the closest pairs within each half and the closest pair between the two
halves.
Sudoku Solver
- Github repo
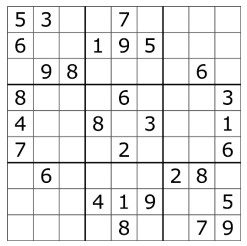
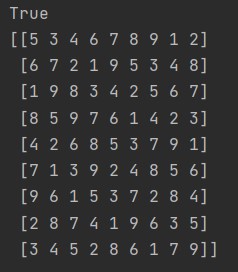
Sudoku is a puzzle in which players insert the numbers one to nine into a grid consisting of nine squares subdivided into a further nine smaller squares in such a way that every number appears once in each horizontal line, vertical line, and square.
we’re solving this puzzle using Backtracking Algorithm.
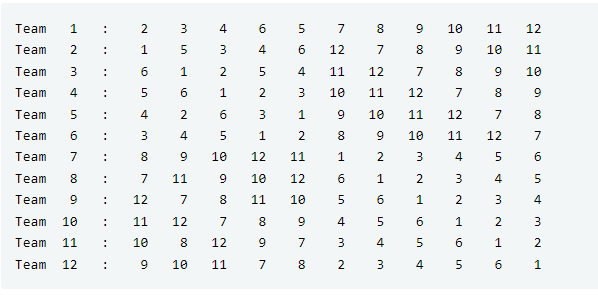
Tournament Scheduler
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
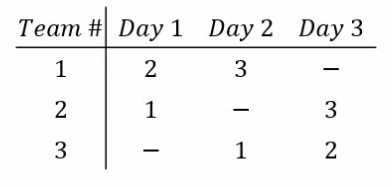
In this problem, we have n sports teams, and these teams want to compete in pairs. The main rule of this problem is that each team can compete only once a day, and now we want to schedule these competitions in such a way that all teams have competed with each other in the shortest amount of days possible.
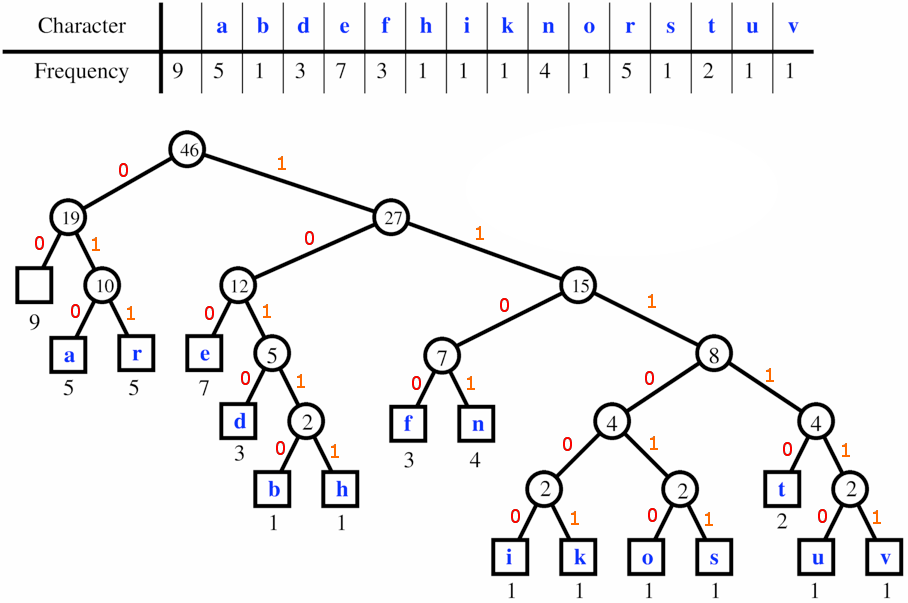
Huffman Coding
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
Huffman Coding is a technique of compressing data to reduce its size without losing any of the details. It was first developed by David Huffman.
Huffman Coding is generally useful to compress the data in which there are frequently occurring characters.
Huffman coding provides an efficient, unambiguous code by analyzing the frequencies that certain symbols appear in a message. Symbols that appear more often will be encoded as a shorter-bit string while symbols that aren’t used as much will be encoded as longer strings. Since the frequencies of symbols vary across messages, there is no one Huffman coding that will work for all messages. This means that the Huffman coding for sending message X may differ from the Huffman coding used to send message Y. There is an algorithm for generating the Huffman coding for a given message based on the frequencies of symbols in that particular message.
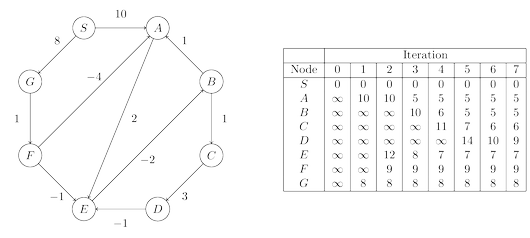
Bellman–Ford
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
Bellman Ford algorithm helps us find the shortest path from a vertex to all other vertices of a weighted graph.
It is similar to Dijkstra’s algorithm but it can work with graphs in which edges can have negative weights.
Bellman Ford algorithm works by overestimating the length of the path from the starting vertex to all other vertices. Then it iteratively relaxes those estimates by finding new paths that are shorter than the previously overestimated paths.
By doing this repeatedly for all vertices, we can guarantee that the result is optimized.
Matrix Chain Multiplication
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
Matrix chain multiplication (or Matrix Chain Ordering Problem, MCOP) is an optimization problem that to find the most efficient way to multiply a given sequence of matrices. The problem is not actually to perform the multiplications but merely to decide the sequence of the matrix multiplications involved.


N-Queens Solver
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
The n-queens problem is a classic combinatorial problem. It is required to place n queens on an n×n chess board so that no two queens threaten each other. Therefore no two queens can be on the same row, column or diagonal. There must be a queen on each column and all their row numbers must differ so a solution can be represented as a permutation of the rows. (Not all permutations are solutions.)
we’re solving this puzzle using Backtracking Algorithm.

Travelling Salesman Problem
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
The travelling salesman problem (also called the travelling salesperson problem or TSP) asks the following question: “Given a list of cities and the distances between each pair of cities, what is the shortest possible route that visits each city exactly once and returns to the origin city?” It is an NP-hard problem in combinatorial optimization, important in theoretical computer science and operations research.