Multiple projects regarding to Artificial Intelligence course
Designing and implementation of:
- BFS, DFS, IDS, UCS (Uninformed Search Strategies)
- 8 Puzzle solver using A* & IDA (Informed
HeuristicSearch Strategies) - genetic algorithms, simulated annealing (Local Search)
- Min-Max, Alpha–Beta (Adversarial Search)
- classification of a dataset (Basic Machine Learning)
- knowledge representation using prolog (knowledge-based system)

BFS, DFS, IDS, UCS (Uninformed Search Strategies)
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
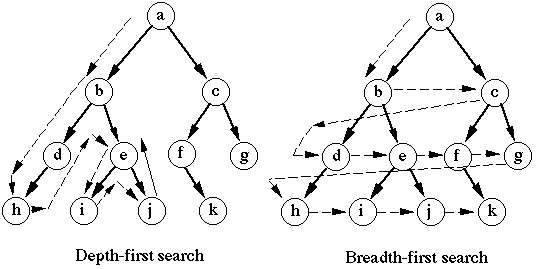
Breadth-first Search(BFS)
- Trees and graphs can be traversed using breadth-first search strategies. It is called breadth-first search because it searches a tree or graph breadthwise.
- Before moving to nodes of the next level, the BFS algorithm searches from the root node of the tree and expands all successor nodes at the current level.
- An example of a general-graph search algorithm is breadth-first search.
- FIFO queue data structure is used for breadth-first search.
Depth-first Search(DFS)
- Trees or graphs can be traversed using depth-first search as a recursive algorithm.
- In depth-first search, each path is followed to its greatest depth node before moving on to the next path.
- In order to implement DFS, a stack data structure is used.
- As with BFS, the DFS algorithm follows a similar process
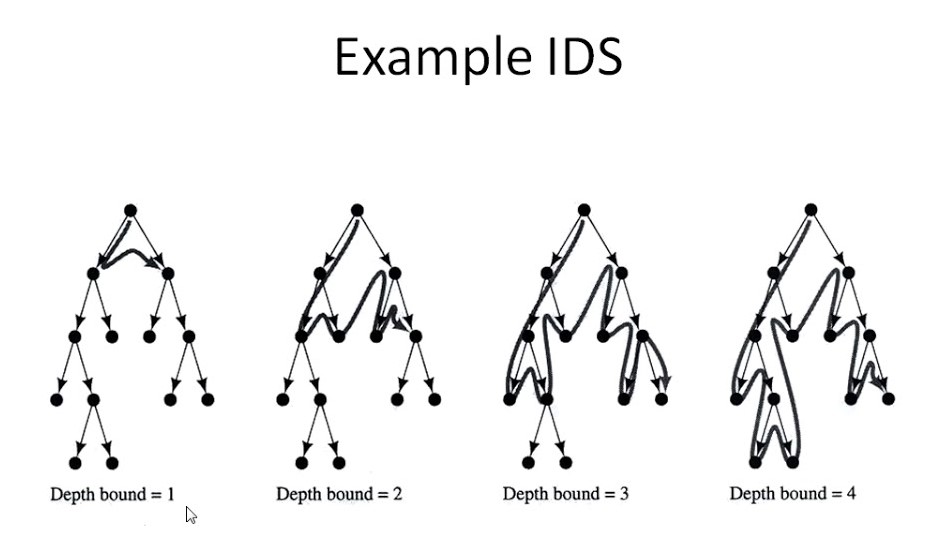
Iterative Deepening Search(IDS)
- By combining depth-first and breadth-first search (for nodes closer to the root), IDS provides efficient space management and fast searching at the same time.
- IDS calls DFS for different depths based on an initial value. Each call of DFS is limited to a given depth. We do DFS in a BFS manner.
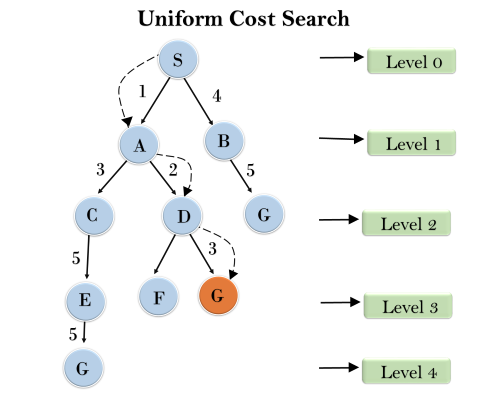
Uniform-cost Search(UCS)
- Uniform-cost search is a searching algorithm used for traversing a weighted tree or graph. When each edge has a different cost, this algorithm is used.
- A uniform-cost search seeks the path with the lowest cumulative cost to the goal node. Using uniform-cost search, nodes are expanded according to their path costs from the root node.
- It can be used to solve any graph/tree where the optimal cost is in demand.
- A uniform-cost search algorithm is implemented by the priority queue.
- It gives maximum priority to the lowest cumulative cost.
- Uniform cost search is equivalent to BFS algorithm if the path cost of all edges is the same.
8 Puzzle solver using A* & IDA (Informed Heuristic Search Strategies)
genetic algorithms, simulated annealing (Local Search)
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
Min-Max, Alpha–Beta (Adversarial Search)
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
classification of a dataset (Basic Machine Learning)
- Code is not available at github at the moment.
knowledge representation using prolog (knowledge-based system)
- Code is not available at github at the moment.